In this guide, I will discuss troubleshooting Windows Stop Codes to fix the dreaded Blue Screen of Death.
Understanding Stop Errors
Start by noting the error code displayed on the blue screen. This code can provide valuable insight into what went wrong with your system.
Next, consider recent changes to your system such as installing new software or updates. Roll back any recent changes that may have triggered the stop error.
If you suspect a hardware issue, check your device drivers and ensure they are up to date. Update or reinstall any drivers that may be causing conflicts.
Perform a memory diagnostic test to check for any memory issues that could be triggering the stop error.
In some cases, a corrupted Windows Update or BIOS firmware can also cause stop errors. Make sure your Windows system and BIOS are updated to the latest versions.
General Troubleshooting Steps
- Restart your computer
- Check for Windows updates
- Update device drivers
- Run a virus scan
- Check for hardware issues
Memory Dump Collection and Analysis
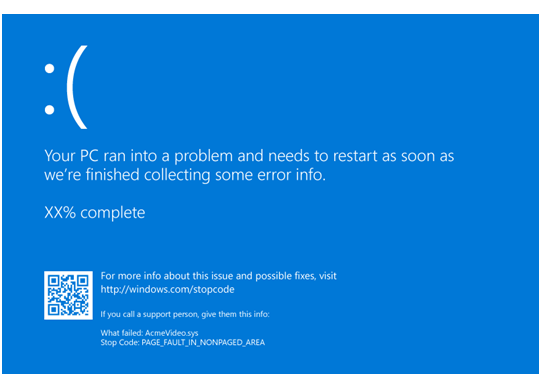
Analysis Tools: Use tools like WinDbg or other debugging tools to analyze the memory dump file. These tools can help identify the root cause of the Stop Code and provide information on which system component or driver may be causing the issue.
Identifying the Cause: Analyzing the memory dump can help pinpoint the specific driver or software that is causing the Blue Screen error. Look for error codes, stack traces, and other relevant information to narrow down the source of the problem.
Resolution: Once you have identified the cause of the Stop Code, you can take appropriate action to resolve the issue. This may involve updating drivers, installing patches, or removing conflicting software.
Advanced Debugging Techniques
To do this, configure your system to create a complete memory dump when a crash occurs. Go to Control Panel > System and Security > System > Advanced system settings > Startup and Recovery, and select “Complete memory dump” under ‘Write debugging information’.
After a crash, use WinDbg to open the memory dump file and analyze it. Look for error messages, codes, and other details that can point you towards the root cause of the problem.
You can also use tools like Windows Performance Recorder to capture detailed information about system behavior leading up to the crash. This can provide valuable insights into what triggered the blue screen.
Additionally, updating device drivers, firmware, and operating system patches can often resolve blue screen errors caused by software bugs or compatibility issues. Make sure to keep your system up to date with the latest updates from Windows Update.
Common Stop Error Codes
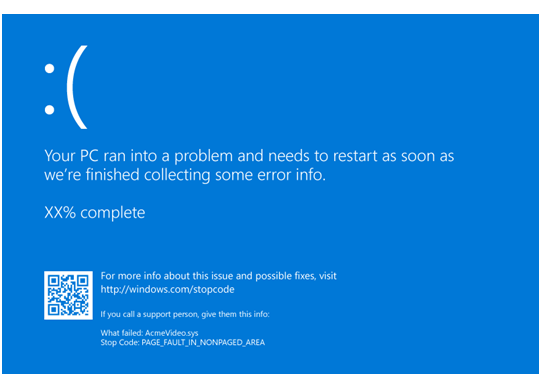
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x0000001A | MEMORY_MANAGEMENT |
| 0x0000003B | SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION |
| 0x00000050 | PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA |
| 0x0000007B | INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE |
| 0x0000007E | SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED |
Booting into Safe Mode with Networking
To boot into Safe Mode with Networking on Windows, follow these steps:
1. Restart your computer.
2. As your computer is booting up, press the F8 key repeatedly until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears.
3. Select “Safe Mode with Networking” using the arrow keys on your keyboard and press Enter.
4. Your computer will now boot into Safe Mode with Networking, allowing you to troubleshoot any issues you may be experiencing, such as the blue screen of death.
By booting into Safe Mode with Networking, you can access the internet and download any necessary patches or updates to fix the issue causing the blue screen error.
Remember to restart your computer normally after troubleshooting in Safe Mode to ensure that the changes take effect.
This method can also help you identify if the issue is related to a specific device driver, software bug, or other factors that may be causing the blue screen error on your Windows system.
Additional Troubleshooting Resources
One option is to check for any recent updates or patches that may have caused the issue. Make sure your Windows 10 operating system is up to date by going to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
Another potential cause of the Blue Screen error could be a corrupt device driver. Update or reinstall your device drivers by going to Device Manager, right-clicking on the relevant driver, and selecting “Update driver.”
If you suspect a software bug or issue with a specific program, try running the program in compatibility mode or reinstalling it to see if that resolves the problem.
In some cases, a memory paging issue could be causing the Blue Screen error. Check your memory usage in Task Manager to see if any programs are using an excessive amount of memory.
Seeking Further Assistance
If you have tried the steps mentioned earlier and are still experiencing the Windows Stop Code error, it may be time to seek further assistance. Here are some additional troubleshooting tips to help you fix the Blue Screen issue:
1. Reach out to Microsoft Support: If you are unable to resolve the problem on your own, contacting Microsoft Support can provide you with expert guidance and solutions tailored to your specific issue.
2. Check for software updates: Make sure your operating system, drivers, and applications are up to date. Sometimes, a simple update can fix the problem causing the Blue Screen error.
3. Run a full system scan: Use a reliable antivirus program to scan your computer for any malware or viruses that may be causing the issue.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I turn off Windows 10 stop code?
To turn off a Windows 10 stop code, force the computer to shut down twice and access Windows Troubleshooting > Advanced Options. If that doesn’t work, create a bootable USB of Windows 10 and boot your computer with it. If the issue persists, perform a clean install.
Can the blue screen of death be fixed?
The blue screen of death can be fixed. When a BSOD occurs, Windows automatically troubleshoots the issue to start repairs.
